Bio-inspired micro-scale surface structures for reducing shockwave-induced flow separation.
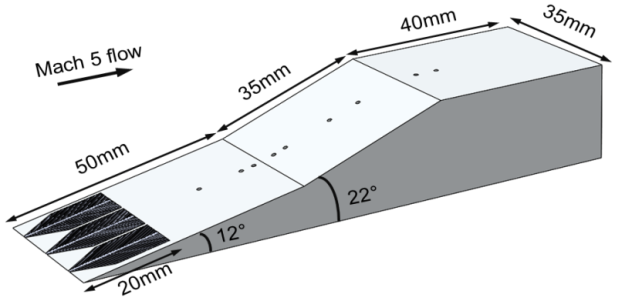
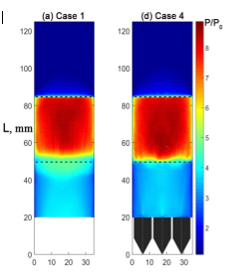
Bio-inspired micro-scale surface structures have been successfully employed to suppress shockwave-induced flow separation for the first time as demonstrated in a wind tunnel experiment undertaken at The University of Manchester. These surface structures were applied behind the leading edge of a double ramp model placed in a Mach 5 freestream leading to a significantly weakened shockwave system and a flow separation bubble with a reduced size as revealed by the high-speed schlieren technique and pressure-sensitive surface coating. This work paves the way for their potential use in controlling shockwave-boundary layer interaction on high-speed vehicles.
Reference:
P Quan, S Zhong, Q Liu, L Li, “Attenuation of Flow Separation Using Herringbone Riblets at M∞=5”. AIAA Journal 57 (1), 142-152.
https://arc.aiaa.org/doi/abs/10.2514/1.J057215?journalCode=aiaaj.